Page 255 - Chemical engineering design
P. 255
PIPING AND INSTRUMENTATION
(a) 231
(b)
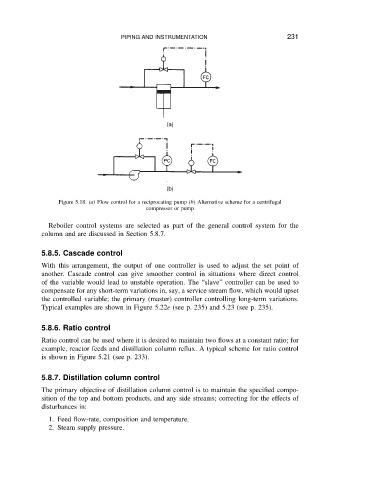
Figure 5.18. (a) Flow control for a reciprocating pump (b) Alternative scheme for a centrifugal
compressor or pump
Reboiler control systems are selected as part of the general control system for the
column and are discussed in Section 5.8.7.
5.8.5. Cascade control
With this arrangement, the output of one controller is used to adjust the set point of
another. Cascade control can give smoother control in situations where direct control
of the variable would lead to unstable operation. The “slave” controller can be used to
compensate for any short-term variations in, say, a service stream flow, which would upset
the controlled variable; the primary (master) controller controlling long-term variations.
Typical examples are shown in Figure 5.22e (see p. 235) and 5.23 (see p. 235).
5.8.6. Ratio control
Ratio control can be used where it is desired to maintain two flows at a constant ratio; for
example, reactor feeds and distillation column reflux. A typical scheme for ratio control
is shown in Figure 5.21 (see p. 233).
5.8.7. Distillation column control
The primary objective of distillation column control is to maintain the specified compo-
sition of the top and bottom products, and any side streams; correcting for the effects of
disturbances in:
1. Feed flow-rate, composition and temperature.
2. Steam supply pressure.