Page 144 - Chemical equilibria Volume 4
P. 144
120 Chemical Equilibria
The standard enthalpy of such a reaction is:
−
1
Δ h 0 = 501.87 kJ.mol
R
2298
We shall now consider the breaking of the second OH bond – i.e. the
following reaction:
OH(gas) = H(gas) + O(gas) [4R.3]
Its standard enthalpy is:
−
1
Δ h 0 = 423.38 kJ.mol
R
3 298
Therefore, we can determine the enthalpy of atomization of water by
finding the sum of the previous two values.
4.2.7.4. Determination of enthalpies of atomization
It is possible to determine the enthalpies of atomization (or dissociation)
of simple gaseous substances such as H 2, O 2, N 2, Cl 2 Br 2, I 2, etc. either by
examining equilibria in which those substances are involved, or on the basis
of spectroscopic data.
We shall look in detail at this latter method, which yields interesting
results because it does not require any temperature measurement to be taken.
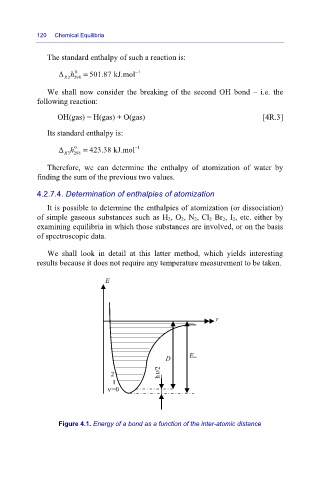
E
r
D E ∞
2 hν/2
1
v=0
Figure 4.1. Energy of a bond as a function of the inter-atomic distance