Page 148 - Chemical equilibria Volume 4
P. 148
124 Chemical Equilibria
We saw earlier that the two O-H bonds in water each had its own energy.
The energy contained in the O-H bond is defined as the mean of those two
values, and more generally the mean of the enthalpies accompanying the
reactions to break such an O-H bond in a large number of compounds. On the
basis of the values we saw in the previous section, this bond energy would be
1
−
ε O-H = 462.3 kJ.mole . This value is, in fact, half of the standard enthalpy of
synthesis of water, which is why knowledge of these enthalpies of synthesis is
valuable.
Thus, it has been possible to attribute a bond energy to a large number of
bonds – particularly in the domain of organic chemistry. Table 4.3 shows a
number of such values, expressed in kJ/mole.
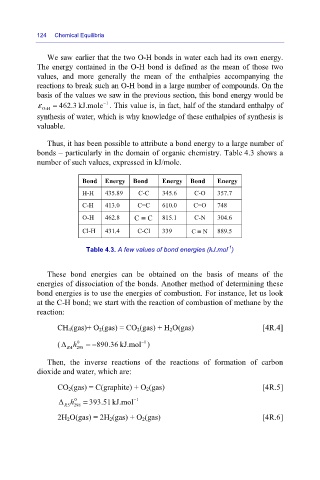
Bond Energy Bond Energy Bond Energy
H-H 435.89 C-C 345.6 C-O 357.7
C-H 413.0 C=C 610.0 C=O 748
O-H 462.8 C ≡ C 815.1 C-N 304.6
Cl-H 431.4 C-Cl 339 C ≡ N 889.5
-1
Table 4.3. A few values of bond energies (kJ.mol )
These bond energies can be obtained on the basis of means of the
energies of dissociation of the bonds. Another method of determining these
bond energies is to use the energies of combustion. For instance, let us look
at the C-H bond; we start with the reaction of combustion of methane by the
reaction:
CH 4(gas)+ O 2(gas) = CO 2(gas) + H 2O(gas) [4R.4]
1
−
( Δ h 0 =− 890.36 kJ.mol )
4298
R
Then, the inverse reactions of the reactions of formation of carbon
dioxide and water, which are:
CO 2(gas) = C(graphite) + O 2(gas) [4R.5]
Δ h 0 = 393.51kJ.mol − 1
5 298
R
2H 2O(gas) = 2H 2(gas) + O 2(gas) [4R.6]