Page 321 - Chemical process engineering design and economics
P. 321
300 Chapter 6
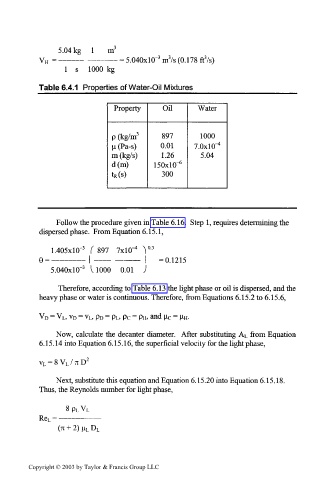
5.04 kg 1 m 3
3
3
3
= ———— ————— = 5.040xlO~ m /s (0.178 ft /s)
V H
1 s 1000 kg
Table 6.4.1 Properties of Water-Oil Mixtures
Property Oil Water
P (kg/m 3 897 1000
n(Pa-s) 0.01 7.0x1 0" 4
m (kg/s) 1.26 5.04
d(m) ISOxlO" 6
t R(s) 300
Follow the procedure given in Table 6.16. Step 1, requires determining the
dispersed phase. From Equation 6.15.1,
1.405xlO~ 897 7X10" , 0.3
e = - = 0.1215
5.040xlO~ 3 UOOO 0.01 )
Therefore, according to Table 6.13 the light phase or oil is dispersed, and the
heavy phase or water is continuous. Therefore, from Equations 6.15.2 to 6.15.6,
V D = V L, V D = V L, p D = p L, p c = p H, and Uc = HH-
Now, calculate the decanter diameter. After substituting A from Equation
L
6.15.14 into Equation 6.15.16, the superficial velocity for the light phase,
v L = 8V L /7iD 2
Next, substitute this equation and Equation 6.15.20 into Equation 6.15.18.
Thus, the Reynolds number for light phase,
8p L V L
Re L = —————
Copyright © 2003 by Taylor & Francis Group LLC