Page 58 - Chemical process engineering design and economics
P. 58
44 Chapter 2
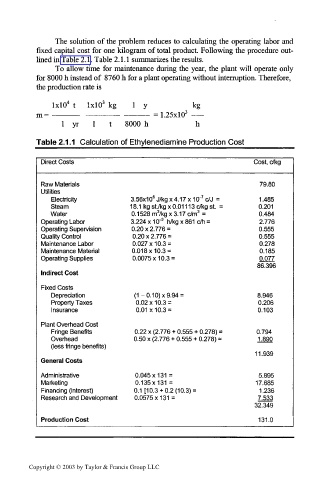
The solution of the problem reduces to calculating the operating labor and
fixed capital cost for one kilogram of total product. Following the procedure out-
lined in Table 2.1. Table 2.1.1 summarizes the results.
To allow time for maintenance during the year, the plant will operate only
for 8000 h instead of 8760 h for a plant operating without interruption. Therefore,
the production rate is
IxlO 4 t IxlO 3 kg 1 y kg
m = — = 1.25xlO J ——
1 yr 1 t 8000 h
Table 2.1.1 Calculation of Ethylenediamine Production Cost
Direct Costs Cost, c/kg
Raw Materials 79.80
Utilities
6
7
Electricity 3.56x10 J/kg x 4.17 x 1tr c/J = 1.485
Steam 1 8. 1 kg st./kg x 0.01 1 1 3 c/kg St. = 0.201
3
Water 0.1528m /kgx3.17c/m 3 = 0.484
Operating Labor 3.224 x10' 3 h/kgx861c/h = 2.776
Operating Supervision 0.20 x 2.776 = 0.555
Quality Control 0.20 x 2.776 = 0.555
Maintenance Labor 0.027x10.3 = 0.278
Maintenance Material 0.018x10.3 = 0.185
Operating Supplies 0.0075x10.3 = 0.077
86.396
Indirect Cost
Fixed Costs
Depreciation (1 - 0.10) x 9.94 = 8.946
Property Taxes 0.02x10.3 = 0.206
Insurance 0.01x10.3 = 0.103
Plant Overhead Cost
Fringe Benefits 0.22 x (2.776 + 0.555 + 0.278) = 0.794
Overhead 0.50 x (2.776 + 0.555 + 0.278) = 1.890
(less fringe benefits)
11.939
General Costs
Administrative 0.045x131 = 5.895
Marketing 0.135x131 = 17.685
Financing (interest) 0.1 [10.3 + 0.2(10.3) = 1.236
Research and Development 0.0575x131 = 7.533
32.349
Production Cost 131.0
Copyright © 2003 by Taylor & Francis Group LLC