Page 54 - Chemical process engineering design and economics
P. 54
40 Chapter 2
2. Ignore pumps and heat exchangers unless substantial loads or unusual
circumstances are involved, such as in a waste-heat boiler or quench tower.
3. Ignore storage unless it involves mechanical handling.
4. Ignore phase separators, such as gravity settlers. These are not significant
process units, but a phase separator containing moving parts, such as a
centrifuge, is considered a process unit.
5. Count mechanical operations, such as crushing, as a process unit.
6. Count utilities if they are specific to the process considered.
Estimates of the number of process units using these guidelines may vary, depend-
ing on the judgment of the process engineer.
Plant Maintenance
Maintenance costs consist of materials, labor, and supervision. Although mainte-
nance cost increases as a plant ages, for economical estimates assume an average
value for the life of the plant. The maintenance cost will vary from 3 to 6% of the
fixed capital cost per year [5]. Use an average value of 4.5%, which consists of
60% labor and 40% materials [5].
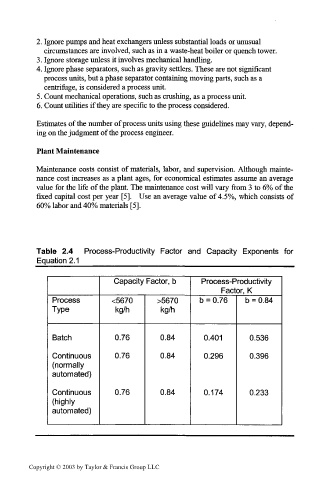
Table 2.4 Process-Productivity Factor and Capacity Exponents for
Equation 2.1 _________
Capacity Factor, b Process-Productivity
Factor, K
Process <5670 >5670 b = 0.76 b = 0.84
Type kg/h kg/h
Batch 0.76 0.84 0.401 0.536
Continuous 0.76 0.84 0.296 0.396
(normally
automated)
Continuous 0.76 0.84 0.174 0.233
(highly
automated)
Copyright © 2003 by Taylor & Francis Group LLC