Page 87 - Chiral Separation Techniques
P. 87
3.6 Library of Cyclic Oligopeptides as Additives to Background Electrolyte … 63
The power of a combinatorial approach to chiral additives for CE was first
demonstrated by Jung and Schurig who used a library of cyclic hexapeptides [74].
Since the number of hexapeptides representing all possible combinations of 20 nat-
6
ural L-amino acids is 64 × 10 , the first study involved only mixed libraries of
hexapeptides of the type c(OOXXXO) consisting of three fixed positions O and
three randomized positions X represented by any of 18 natural amino acids (cys-
teine and tryptophan were not included into the scheme). Three cyclopeptide
libraries c(L-Asp-L-Phe-XXX-D-Ala), c(L-Arg-L-Lys-XXX-D-Ala), and
c(L-Arg-L-Met-XXX-D-Ala), each consisting of 5832 members, were prepared and
tested in chiral CE. When dissolved in an electrolyte to form 10 mmol/L solutions,
all three libraries enabled the separation of racemates. For example, the first library
facilitated the baseline separation of racemic Tröger’s base in a 67 cm-long capillary
with a selectivity factor α of 1.01 and column efficiency of 360 000 plates. Similarly,
the second library helped to resolve the N-2,4-dinitrophenyl (DNP) derivative of glu-
tamic acid in a capillary with the same length affording a selectivity factor of 1.13
and a column efficiency of 79 000 plates. These results indicate the presence of use-
ful selectors in the mixed library. However, this brief study did not attempt the
deconvolution of the mixture and did not identify the best selector.
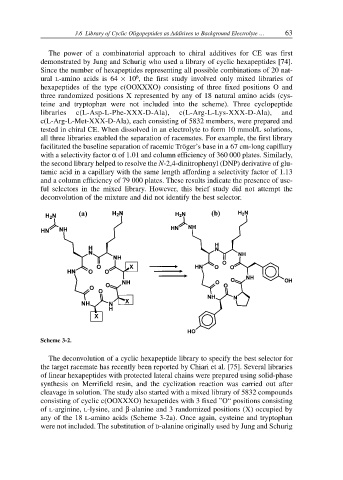
Scheme 3-2.
The deconvolution of a cyclic hexapeptide library to specify the best selector for
the target racemate has recently been reported by Chiari et al. [75]. Several libraries
of linear hexapeptides with protected lateral chains were prepared using solid-phase
synthesis on Merrifield resin, and the cyclization reaction was carried out after
cleavage in solution. The study also started with a mixed library of 5832 compounds
consisting of cyclic c(OOXXXO) hexapetides with 3 fixed ”O“ positions consisting
of L-arginine, L-lysine, and β-alanine and 3 randomized positions (X) occupied by
any of the 18 L-amino acids (Scheme 3-2a). Once again, cysteine and tryptophan
were not included. The substitution of D-alanine originally used by Jung and Schurig