Page 30 - Color Atlas of Biochemistry
P. 30
Physical Chemistry 21
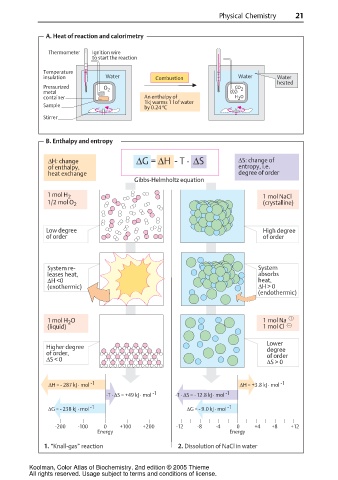
A. Heat of reaction and calorimetry
Thermometer Ignition wire
to start the reaction
6 6
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 1 2 1
Temperature 1 1
2 3 2 3
insulation 4 5 Water Combustion 4 5 Water Water
6 6
heated
Pressurized O 2 CO 2
metal
container An enthalpy of H O
2
1kJ warms 1 l of water
Sample by 0.24 ºC
Stirrer
B. Enthalpy and entropy
∆H: change ∆G = ∆H - T · ∆S ∆S: change of
of enthalpy, entropy, i.e.
heat exchange degree of order
Gibbs-Helmholtz equation
1 mol H 2 1 mol NaCl
1/2 mol O 2 (crystalline)
Low degree High degree
of order of order
System re- System
leases heat, absorbs
∆H <0 heat,
(exothermic) ∆H > 0
(endothermic)
1 mol H O 1 mol Na
2
(liquid) 1 mol Cl
Lower
Higher degree degree
of order, of order
∆S < 0 ∆S > 0
∆H = - 287 kJ · mol -1 ∆H = +3.8 kJ · mol -1
-T · ∆S = +49 kJ · mol -1 -T · ∆S = - 12.8 kJ · mol -1
∆G = - 238 kJ · mol -1 ∆G = - 9.0 kJ · mol -1
-200 -100 0 +100 +200 -12 -8 -4 0 +4 +8 +12
Energy Energy
1. “Knall-gas” reaction 2. Dissolution of NaCl in water
Koolman, Color Atlas of Biochemistry, 2nd edition © 2005 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.