Page 13 - Complete Wireless Design
P. 13
Wireless Essentials
12 Chapter One
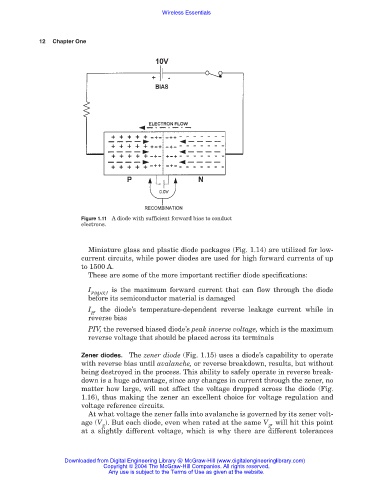
Figure 1.11 A diode with sufficient forward bias to conduct
electrons.
Miniature glass and plastic diode packages (Fig. 1.14) are utilized for low-
current circuits, while power diodes are used for high forward currents of up
to 1500 A.
These are some of the more important rectifier diode specifications:
I , is the maximum forward current that can flow through the diode
F(MAX)
before its semiconductor material is damaged
I , the diode’s temperature-dependent reverse leakage current while in
R
reverse bias
PIV, the reversed biased diode’s peak inverse voltage, which is the maximum
reverse voltage that should be placed across its terminals
Zener diodes. The zener diode (Fig. 1.15) uses a diode’s capability to operate
with reverse bias until avalanche, or reverse breakdown, results, but without
being destroyed in the process. This ability to safely operate in reverse break-
down is a huge advantage, since any changes in current through the zener, no
matter how large, will not affect the voltage dropped across the diode (Fig.
1.16), thus making the zener an excellent choice for voltage regulation and
voltage reference circuits.
At what voltage the zener falls into avalanche is governed by its zener volt-
age (V ). But each diode, even when rated at the same V , will hit this point
Z Z
at a slightly different voltage, which is why there are different tolerances
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.