Page 347 - Compression Machinery for Oil and Gas
P. 347
332 SECTION II Types of Equipment
100
80
% Torque 60 Centrifugal compressor 1
Centrifugal compressor 2
40
20
0
0 20 40 60 80 100
% Synch speed
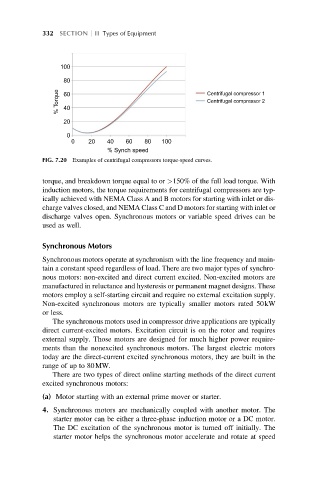
FIG. 7.20 Examples of centrifugal compressors torque-speed curves.
torque, and breakdown torque equal to or >150% of the full load torque. With
induction motors, the torque requirements for centrifugal compressors are typ-
ically achieved with NEMA Class A and B motors for starting with inlet or dis-
charge valves closed, and NEMA Class C and D motors for starting with inlet or
discharge valves open. Synchronous motors or variable speed drives can be
used as well.
Synchronous Motors
Synchronous motors operate at synchronism with the line frequency and main-
tain a constant speed regardless of load. There are two major types of synchro-
nous motors: non-excited and direct current excited. Non-excited motors are
manufactured in reluctance and hysteresis or permanent magnet designs. These
motors employ a self-starting circuit and require no external excitation supply.
Non-excited synchronous motors are typically smaller motors rated 50kW
or less.
The synchronous motors used in compressor drive applications are typically
direct current-excited motors. Excitation circuit is on the rotor and requires
external supply. Those motors are designed for much higher power require-
ments than the nonexcited synchronous motors. The largest electric motors
today are the direct-current excited synchronous motors, they are built in the
range of up to 80MW.
There are two types of direct online starting methods of the direct current
excited synchronous motors:
(a) Motor starting with an external prime mover or starter.
4. Synchronous motors are mechanically coupled with another motor. The
starter motor can be either a three-phase induction motor or a DC motor.
The DC excitation of the synchronous motor is turned off initially. The
starter motor helps the synchronous motor accelerate and rotate at speed