Page 346 - Compression Machinery for Oil and Gas
P. 346
Drivers Chapter 7 331
% Speed vs % torque 2 throw starting at 800
psi unloaded using bypass
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
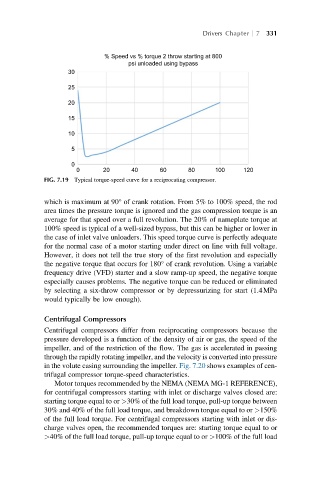
FIG. 7.19 Typical torque-speed curve for a reciprocating compressor.
which is maximum at 90° of crank rotation. From 5% to 100% speed, the rod
area times the pressure torque is ignored and the gas compression torque is an
average for that speed over a full revolution. The 20% of nameplate torque at
100% speed is typical of a well-sized bypass, but this can be higher or lower in
the case of inlet valve unloaders. This speed torque curve is perfectly adequate
for the normal case of a motor starting under direct on line with full voltage.
However, it does not tell the true story of the first revolution and especially
the negative torque that occurs for 180° of crank revolution. Using a variable
frequency drive (VFD) starter and a slow ramp-up speed, the negative torque
especially causes problems. The negative torque can be reduced or eliminated
by selecting a six-throw compressor or by depressurizing for start (1.4MPa
would typically be low enough).
Centrifugal Compressors
Centrifugal compressors differ from reciprocating compressors because the
pressure developed is a function of the density of air or gas, the speed of the
impeller, and of the restriction of the flow. The gas is accelerated in passing
through the rapidly rotating impeller, and the velocity is converted into pressure
in the volute casing surrounding the impeller. Fig. 7.20 shows examples of cen-
trifugal compressor torque-speed characteristics.
Motor torques recommended by the NEMA (NEMA MG-1 REFERENCE),
for centrifugal compressors starting with inlet or discharge valves closed are:
starting torque equal to or >30% of the full load torque, pull-up torque between
30% and 40% of the full load torque, and breakdown torque equal to or >150%
of the full load torque. For centrifugal compressors starting with inlet or dis-
charge valves open, the recommended torques are: starting torque equal to or
>40% of the full load torque, pull-up torque equal to or >100% of the full load