Page 181 - Computational Colour Science Using MATLAB
P. 181
168 MULTISPECTRAL IMAGING
the singular value decomposition of this matrix that yield the principal
components. In practice, however, it is not always necessary to subtract the
mean to use a linear model of reflectance. If we use a linear model to represent a
set of reflectance spectra, then a given sample in the set is given by the linear sum
of the basis functions weighted by coefficients so that
PðlÞ¼ a 1 B 1 ðlÞþ a 2 B 2 ðlÞþ a 3 B 3 ðlÞ :: : a n B n ðlÞ, ð10.9Þ
and if all n basis functions are used all the spectra in the set can be reconstructed
perfectly using appropriate values of the weights a .. . a . However, the benefit of
1
n
techniques such as PCA is that it is possible to represent data efficiently by only
using a small number of basis functions. The first basis function maximally
represents the variance in the data, and subsequent basis functions maximally
represent the remaining variance. It has been shown that more than 95% of the
variance in a set of reflectance spectra can be represented by using just the first
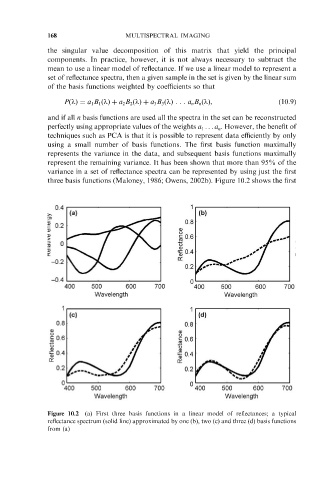
three basis functions (Maloney, 1986; Owens, 2002b). Figure 10.2 shows the first
Figure 10.2 (a) First three basis functions in a linear model of reflectances; a typical
reflectance spectrum (solid line) approximated by one (b), two (c) and three (d) basis functions
from (a)