Page 200 - Computational Modeling in Biomedical Engineering and Medical Physics
P. 200
Magnetic drug targeting 189
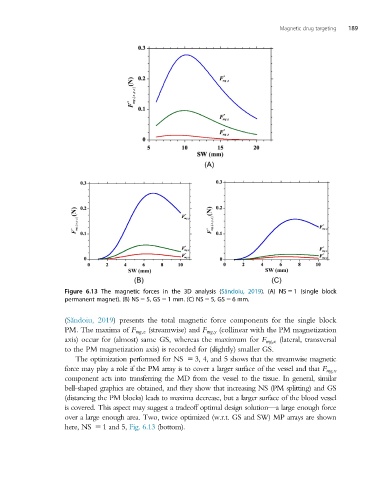
Figure 6.13 The magnetic forces in the 3D analysis (S˘ andoiu, 2019). (A) NS 5 1 (single block
permanent magnet). (B) NS 5 5, GS 5 1 mm. (C) NS 5 5, GS 5 6 mm.
(S˘ andoiu, 2019) presents the total magnetic force components for the single block
PM. The maxima of F mg;z (streamwise) and F mg;y (collinear with the PM magnetization
axis) occur for (almost) same GS, whereas the maximum for F mg;x (lateral, transversal
to the PM magnetization axis) is recorded for (slightly) smaller GS.
The optimization performed for NS 5 3, 4, and 5 shows that the streamwise magnetic
force may play a role if the PM array is to cover a larger surface of the vessel and that F mg,x
component acts into transferring the MD from the vessel to the tissue. In general, similar
bell-shaped graphics are obtained, and they show that increasing NS (PM splitting) and GS
(distancing the PM blocks) leads to maxima decrease, but a larger surface of the blood vessel
is covered. This aspect may suggest a tradeoff optimal design solution—a large enough force
over a large enough area. Two, twice optimized (w.r.t. GS and SW) MP arrays are shown
here, NS 5 1and 5, Fig. 6.13 (bottom).