Page 218 - Computational Modeling in Biomedical Engineering and Medical Physics
P. 218
Magnetic drug targeting 207
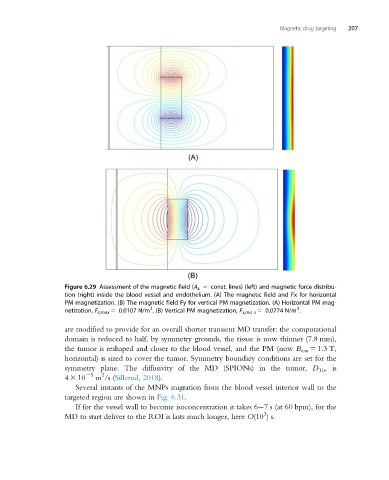
Figure 6.29 Assessment of the magnetic field (A z 5 const. lines) (left) and magnetic force distribu-
tion (right) inside the blood vessel and endothelium. (A) The magnetic field and Fx for horizontal
PM magnetization. (B) The magnetic field Fy for vertical PM magnetization. (A) Horizontal PM mag-
3
3
netization, F x,max 5 0.0107 N/m . (B) Vertical PM magnetization, F x,ma x 5 0.0774 N/m .
are modified to provide for an overall shorter transient MD transfer: the computational
domain is reduced to half, by symmetry grounds, the tissue is now thinner (7.8 mm),
the tumor is reshaped and closer to the blood vessel, and the PM (now B rem 5 1.3 T,
horizontal) is sized to cover the tumor. Symmetry boundary conditions are set for the
symmetry plane. The diffusivity of the MD (SPIONs) in the tumor, D Tu ,is
2
4 3 10 25 m /s (Sillerud, 2018).
Several instants of the MNPs migration from the blood vessel interior wall to the
targeted region are shown in Fig. 6.31.
If for the vessel wall to become isoconcentration it takes 6 7 s (at 60 bpm), for the
3
MD to start deliver to the ROI is lasts much longer, here O(10 )s.