Page 277 - Computational Retinal Image Analysis
P. 277
1 Introduction 275
treatment, studies have demonstrated that tolerating a small amount of SRF may be
feasible in the management of these diseases [12].
Sub-RPE fluid in PED
These lesions can be subdivided into serous PED containing solely fluid and fibrovascu-
lar PED containing both fluid and fibrovascular tissue. Hence, sub-RPE fluid can either
be a sub-RPE space that is homogeneously hyporeflective in serous PED or within fibro-
vascular PED that exhibit a more heterogeneous pattern with hyporeflective and hyper-
reflective areas. If a PED is purely hyperreflective without any hyporeflective elements,
it is said not to contain any sub-RPE fluid. PED occur primarily in patients with nAMD.
Sub-RPE fluid is a sign of active choroidal neovascularization. Any increasing sub-RPE
fluid should be regarded a retreatment indication. As long as the sub-RPE fluid is covered
by intact pigment epithelium, it is not associated with substantial vision loss [11].
Manual assessment of fluid with OCT is subjective and has become prohibitively
time consuming due to large numbers of fluid pockets and B-scans acquired by the
modern OCT that need to be visually analyzed. This calls for the development of
computational retinal image analysis methods that can objectively and repeatedly
detect and quantify fluid from OCT datasets. However, automated image analysis of
OCT scans is hindered by OCT’s anisotropic resolution, motion artifacts, and low
signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) due to speckle [13]. Furthermore, there is a substantial
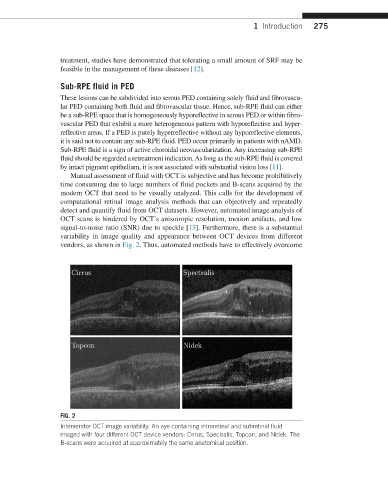
variability in image quality and appearance between OCT devices from different
vendors, as shown in Fig. 2. Thus, automated methods have to effectively overcome
FIG. 2
Intervendor OCT image variability. An eye containing intraretinal and subretinal fluid
imaged with four different OCT device vendors: Cirrus, Spectralis, Topcon, and Nidek. The
B-scans were acquired at approximately the same anatomical position.