Page 115 - Computational Statistics Handbook with MATLAB
P. 115
102 Computational Statistics Handbook with MATLAB
end
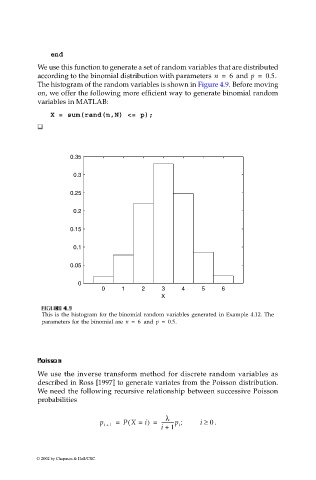
We use this function to generate a set of random variables that are distributed
according to the binomial distribution with parameters n = 6 and p = 0.5.
The histogram of the random variables is shown in Figure 4.9. Before moving
on, we offer the following more efficient way to generate binomial random
variables in MATLAB:
X = sum(rand(n,N) <= p);
0.35
0.3
0.25
0.2
0.15
0.1
0.05
0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
X
IG
F FI U URE G 4. RE 4. 9 9
9
GU
F F II GU RE RE 4. 4. 9
This is the histogram for the binomial random variables generated in Example 4.12. The
parameters for the binomial are n = 6 and p = 0.5.
PPooii
Po
Poi isssoson n
nn
sssoso
We use the inverse transform method for discrete random variables as
described in Ross [1997] to generate variates from the Poisson distribution.
We need the following recursive relationship between successive Poisson
probabilities
λ
(
p i + 1 = PX = i) = -----------p ; i ≥ . 0
i
i + 1
© 2002 by Chapman & Hall/CRC