Page 114 - Computational Statistics Handbook with MATLAB
P. 114
Chapter 4: Generating Random Variables 101
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
X 2 0
−0.2
−0.4
−0.6
−0.8
−1 −0.5 0 0.5 1
X
1
F FI U URE G 4. RE 4. 8 8
IG
8
F F II GU RE RE 4. 4. 8
GU
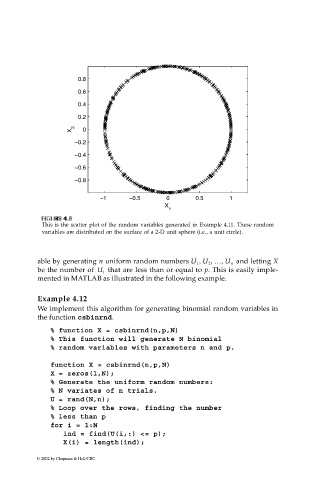
This is the scatter plot of the random variables generated in Example 4.11. These random
variables are distributed on the surface of a 2-D unit sphere (i.e., a unit circle).
, , , and letting X
able by generating n uniform random numbers U 1 U 2 … U n
that are less than or equal to p. This is easily imple-
be the number of U i
mented in MATLAB as illustrated in the following example.
Example 4.12
We implement this algorithm for generating binomial random variables in
the function csbinrnd.
% function X = csbinrnd(n,p,N)
% This function will generate N binomial
% random variables with parameters n and p.
function X = csbinrnd(n,p,N)
X = zeros(1,N);
% Generate the uniform random numbers:
% N variates of n trials.
U = rand(N,n);
% Loop over the rows, finding the number
% less than p
for i = 1:N
ind = find(U(i,:) <= p);
X(i) = length(ind);
© 2002 by Chapman & Hall/CRC