Page 185 - Computational Statistics Handbook with MATLAB
P. 185
172 Computational Statistics Handbook with MATLAB
6
4
2
0
−2
−4
−6
−6 −4 −2 0 2 4 6
IG
F FI U URE G 5.4 RE 5.4 4 4
5.4
GU
F F II GU RE RE 5.4 4 4
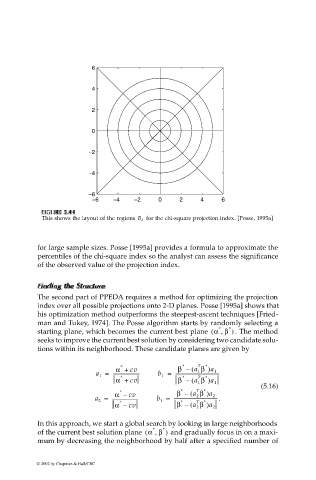
for the chi-square projection index. [Posse, 1995a]
This shows the layout of the regions B k
for large sample sizes. Posse [1995a] provides a formula to approximate the
percentiles of the chi-square index so the analyst can assess the significance
of the observed value of the projection index.
r
t
ct
ree
ruuc
t
t
Findingt
FFindinginding
Finding thheSteS rr uucctt tuur uurr ee
tt
hheSeS
The second part of PPEDA requires a method for optimizing the projection
index over all possible projections onto 2-D planes. Posse [1995a] shows that
his optimization method outperforms the steepest-ascent techniques [Fried-
man and Tukey, 1974]. The Posse algorithm starts by randomly selecting a
starting plane, which becomes the current best plane α β,( * * ) . The method
seeks to improve the current best solution by considering two candidate solu-
tions within its neighborhood. These candidate planes are given by
* * ( T *
α + cv β – a 1 β )a 1
a 1 = ---------------------- b 1 = ------------------------------------
*
*
T
*
α + cv β – ( a 1 β )a 1
(5.16)
* * ( T *
α – cv β – a 2 β )a 2
a 2 = ---------------------- b 1 = ------------------------------------.
T
*
*
*
α – cv β – ( a 2 β )a 2
In this approach, we start a global search by looking in large neighborhoods
of the current best solution plane α β,( * * ) and gradually focus in on a maxi-
mum by decreasing the neighborhood by half after a specified number of
© 2002 by Chapman & Hall/CRC