Page 355 - Computational Statistics Handbook with MATLAB
P. 355
344 Computational Statistics Handbook with MATLAB
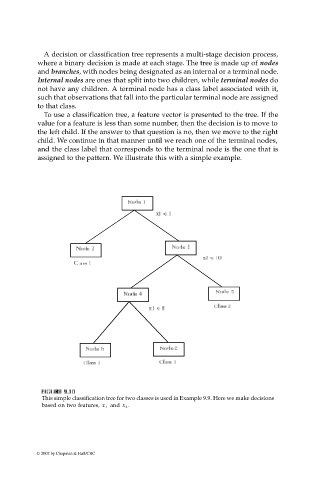
A decision or classification tree represents a multi-stage decision process,
where a binary decision is made at each stage. The tree is made up of nodes
and branches, with nodes being designated as an internal or a terminal node.
Internal nodes are ones that split into two children, while terminal nodes do
not have any children. A terminal node has a class label associated with it,
such that observations that fall into the particular terminal node are assigned
to that class.
To use a classification tree, a feature vector is presented to the tree. If the
value for a feature is less than some number, then the decision is to move to
the left child. If the answer to that question is no, then we move to the right
child. We continue in that manner until we reach one of the terminal nodes,
and the class label that corresponds to the terminal node is the one that is
assigned to the pattern. We illustrate this with a simple example.
de No 1
x1 < 5
de No 3
No de 2
2<1
0
x
Class 1
Node 5
Nod e 4
s Clas 2
1<8
x
e Nod 7
Nod e 6
s Clas 1
s Clas 2
IG
GU
F F FI F U URE GU 9.1 RE RE RE 9.1 0 0 0 0
II
9.1
9.1
G
This simple classification tree for two classes is used in Example 9.9. Here we make decisions
and x 2 .
based on two features, x 1
© 2002 by Chapman & Hall/CRC