Page 111 -
P. 111
84 CHAPTER 3 / A TOP-LEVEL VIEW OF COMPUTER FUNCTION
Read
Memory
Write
N words
0 Data
Address
•
•
•
Data N – 1
Read
I/O module Internal
Write data
External
Address M ports data
Internal
data Interrupt
signals
External
data
Instructions Address
Control
Data CPU signals
Interrupt Data
signals
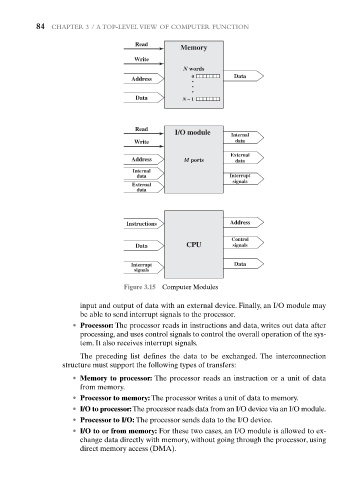
Figure 3.15 Computer Modules
input and output of data with an external device. Finally, an I/O module may
be able to send interrupt signals to the processor.
• Processor: The processor reads in instructions and data, writes out data after
processing, and uses control signals to control the overall operation of the sys-
tem. It also receives interrupt signals.
The preceding list defines the data to be exchanged. The interconnection
structure must support the following types of transfers:
• Memory to processor: The processor reads an instruction or a unit of data
from memory.
• Processor to memory: The processor writes a unit of data to memory.
• I/O to processor:The processor reads data from an I/O device via an I/O module.
• Processor to I/O: The processor sends data to the I/O device.
• I/O to or from memory: For these two cases, an I/O module is allowed to ex-
change data directly with memory, without going through the processor, using
direct memory access (DMA).