Page 289 -
P. 289
268 5 Segmentation
(a) (b)
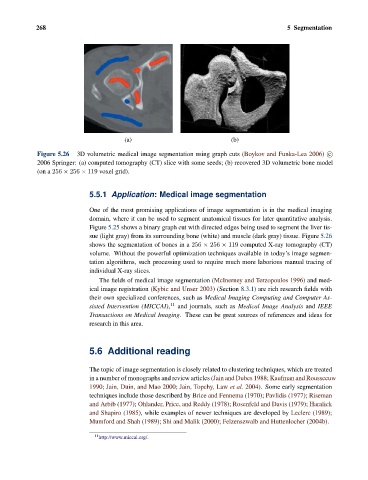
Figure 5.26 3D volumetric medical image segmentation using graph cuts (Boykov and Funka-Lea 2006) c
2006 Springer: (a) computed tomography (CT) slice with some seeds; (b) recovered 3D volumetric bone model
(on a 256 × 256 × 119 voxel grid).
5.5.1 Application: Medical image segmentation
One of the most promising applications of image segmentation is in the medical imaging
domain, where it can be used to segment anatomical tissues for later quantitative analysis.
Figure 5.25 shows a binary graph cut with directed edges being used to segment the liver tis-
sue (light gray) from its surrounding bone (white) and muscle (dark gray) tissue. Figure 5.26
shows the segmentation of bones in a 256 × 256 × 119 computed X-ray tomography (CT)
volume. Without the powerful optimization techniques available in today’s image segmen-
tation algorithms, such processing used to require much more laborious manual tracing of
individual X-ray slices.
The fields of medical image segmentation (McInerney and Terzopoulos 1996) and med-
ical image registration (Kybic and Unser 2003) (Section 8.3.1) are rich research fields with
their own specialized conferences, such as Medical Imaging Computing and Computer As-
sisted Intervention (MICCAI), 11 and journals, such as Medical Image Analysis and IEEE
Transactions on Medical Imaging. These can be great sources of references and ideas for
research in this area.
5.6 Additional reading
The topic of image segmentation is closely related to clustering techniques, which are treated
in a number of monographs and review articles (Jain and Dubes 1988; Kaufman and Rousseeuw
1990; Jain, Duin, and Mao 2000; Jain, Topchy, Law et al. 2004). Some early segmentation
techniques include those describerd by Brice and Fennema (1970); Pavlidis (1977); Riseman
and Arbib (1977); Ohlander, Price, and Reddy (1978); Rosenfeld and Davis (1979); Haralick
and Shapiro (1985), while examples of newer techniques are developed by Leclerc (1989);
Mumford and Shah (1989); Shi and Malik (2000); Felzenszwalb and Huttenlocher (2004b).
11 http://www.miccai.org/.