Page 142 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 142
Global Positioning System (GPS)
GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEM (GPS)
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a network of wireless location and
navigation apparatus that operates on a worldwide basis.The GPS employs
several satellites, and allows determination of latitude, longitude, and
altitude. It is used in some mobile robotic systems for guidance when
extreme, localized precision is not necessary.
All GPS satellites transmit signals in the ultra-high-frequency (UHF)
radio spectrum. The signals are modulated with codes that contain tim-
ing information used by the receiving apparatus to make measurements.
A GPS receiver determines its location by measuring the distances to
four or more different satellites, and using a computer to process the in-
formation received from the satellites. From this information the re-
ceiver can give the user an indication of position accurate to within a
few meters.
See also DISTANCE MEASUREMENT.
GRACEFUL DEGRADATION
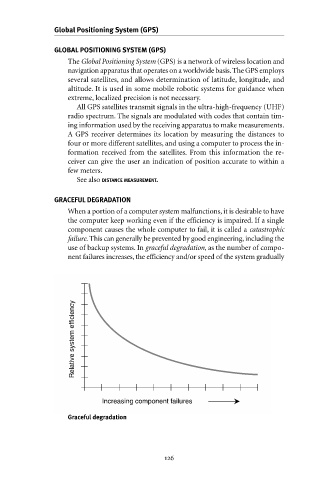
When a portion of a computer system malfunctions, it is desirable to have
the computer keep working even if the efficiency is impaired. If a single
component causes the whole computer to fail, it is called a catastrophic
failure. This can generally be prevented by good engineering, including the
use of backup systems. In graceful degradation, as the number of compo-
nent failures increases, the efficiency and/or speed of the system gradually
Relative system efficiency
Increasing component failures
Graceful degradation