Page 143 - Concise Encyclopedia of Robotics
P. 143
Graphical Path Planning
declines, but does not instantly drop to zero. The illustration is a graph of
the behavior of a hypothetical robotic system with graceful degradation.
In the event of a subsystem malfunction, a sophisticated computer or
robot controller can use other circuits to accomplish the tasks of the failed
part of the system temporarily.The human operator or attendant is notified
that something is wrong, and technicians can fix it, often with little or no
downtime. Compare FAULT RESILIENCE.
GRAPHICAL PATH PLANNING
Graphical path planning is a method of navigation used by mobile robots.
It is a specialized scheme or set of schemes for the execution of metric
path planning. In graphical path planning, all possible routes are plotted
on a computer map of the work environment. These routes can be chosen
in various ways, by employing specific algorithms.
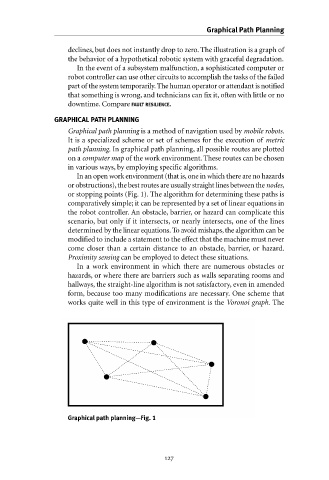
In an open work environment (that is,one in which there are no hazards
or obstructions),the best routes are usually straight lines between the nodes,
or stopping points (Fig. 1). The algorithm for determining these paths is
comparatively simple; it can be represented by a set of linear equations in
the robot controller. An obstacle, barrier, or hazard can complicate this
scenario, but only if it intersects, or nearly intersects, one of the lines
determined by the linear equations.To avoid mishaps,the algorithm can be
modified to include a statement to the effect that the machine must never
come closer than a certain distance to an obstacle, barrier, or hazard.
Proximity sensing can be employed to detect these situations.
In a work environment in which there are numerous obstacles or
hazards, or where there are barriers such as walls separating rooms and
hallways, the straight-line algorithm is not satisfactory, even in amended
form, because too many modifications are necessary. One scheme that
works quite well in this type of environment is the Voronoi graph. The
Graphical path planning—Fig. 1