Page 172 - Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering
P. 172
Medical robotics 157
Documents by year
400
350
300
Documents 250
200
150
100
50
0
1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2010 2012 2014 2016 2018 2020
Year
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. Scopus® is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V.
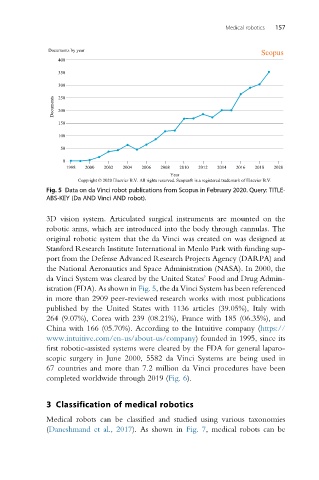
Fig. 5 Data on da Vinci robot publications from Scopus in February 2020. Query: TITLE-
ABS-KEY (Da AND Vinci AND robot).
3D vision system. Articulated surgical instruments are mounted on the
robotic arms, which are introduced into the body through cannulas. The
original robotic system that the da Vinci was created on was designed at
Stanford Research Institute International in Menlo Park with funding sup-
port from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and
the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). In 2000, the
da Vinci System was cleared by the United States’ Food and Drug Admin-
istration (FDA). As shown in Fig. 5, the da Vinci System has been referenced
in more than 2909 peer-reviewed research works with most publications
published by the United States with 1136 articles (39.05%), Italy with
264 (9.07%), Corea with 239 (08.21%), France with 185 (06.35%), and
China with 166 (05.70%). According to the Intuitive company (https://
www.intuitive.com/en-us/about-us/company) founded in 1995, since its
first robotic-assisted systems were cleared by the FDA for general laparo-
scopic surgery in June 2000, 5582 da Vinci Systems are being used in
67 countries and more than 7.2 million da Vinci procedures have been
completed worldwide through 2019 (Fig. 6).
3 Classification of medical robotics
Medical robots can be classified and studied using various taxonomies
(Daneshmand et al., 2017). As shown in Fig. 7, medical robots can be