Page 169 - Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering
P. 169
154 Control theory in biomedical engineering
sensing systems that provide them with safety features (Troccaz et al., 1995;
Davies, 1996; Fei et al., 2001). Although medical robotics offer many advan-
tages, it is recognized by many authors that the acceptance of robots in
healthcare has been slowed by safety concerns (Preising et al., 1991). To
be accepted and widely deployed, medical robots have to provide real
advantages, including reduction of access trauma, faster recovery, scar
limitation, cost reduction, eases of use, human-machine communication
capabilities, and so on.
This chapter gives a comprehensive review of the current literature on
medical robotics and highlights the different classification approaches related
to medical robots. It also stresses fundamental requirements like safety.
Finally, the chapter presents the main applications of medical robots such
as in surgery, rehabilitation, and training.
2 Literature review
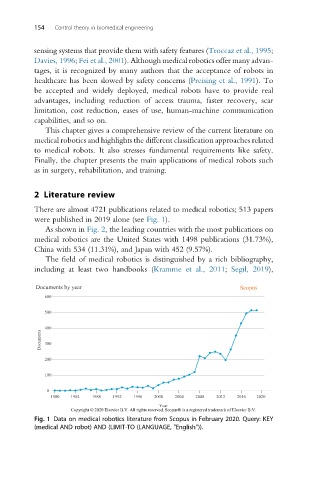
There are almost 4721 publications related to medical robotics; 513 papers
were published in 2019 alone (see Fig. 1).
As shown in Fig. 2, the leading countries with the most publications on
medical robotics are the United States with 1498 publications (31.73%),
China with 534 (11.31%), and Japan with 452 (9.57%).
The field of medical robotics is distinguished by a rich bibliography,
including at least two handbooks (Kramme et al., 2011; Segil, 2019),
Fig. 1 Data on medical robotics literature from Scopus in February 2020. Query: KEY
(medical AND robot) AND (LIMIT-TO (LANGUAGE, "English”)).