Page 178 - Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering
P. 178
Medical robotics 163
– recording and understanding data as valuable tools for training, skill
assessment, and certification for surgeons;
– keeping immune to infection;
– being potentially unaffected by radiation; and
– ability to incorporate many sensors (force, acoustic, etc.).
4.2 Fundamental requirements
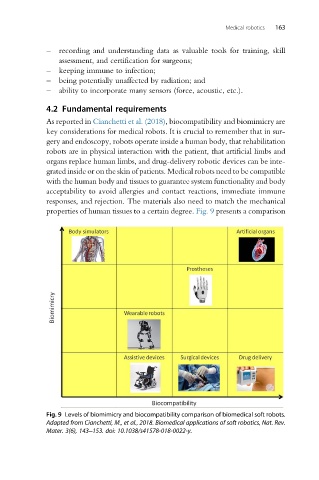
As reported in Cianchetti et al. (2018), biocompatibility and biomimicry are
key considerations for medical robots. It is crucial to remember that in sur-
gery and endoscopy, robots operate inside a human body, that rehabilitation
robots are in physical interaction with the patient, that artificial limbs and
organs replace human limbs, and drug-delivery robotic devices can be inte-
grated inside or on the skin of patients. Medical robots need to be compatible
with the human body and tissues to guarantee system functionality and body
acceptability to avoid allergies and contact reactions, immediate immune
responses, and rejection. The materials also need to match the mechanical
properties of human tissues to a certain degree. Fig. 9 presents a comparison
Fig. 9 Levels of biomimicry and biocompatibility comparison of biomedical soft robots.
Adapted from Cianchetti, M., et al., 2018. Biomedical applications of soft robotics, Nat. Rev.
Mater. 3(6), 143–153. doi: 10.1038/s41578-018-0022-y.