Page 58 - Control Theory in Biomedical Engineering
P. 58
Mathematical modeling of cholesterol homeostasis 45
of them is a universal remedy due to various side effects. However, due to
the development of various mathematical models, it is possible to predict the
cause of the disorder in cholesterol metabolism and optimize the conditions
to reduce its effects on the body.
In this study, we present a two-compartment ordinary differential
equation (ODE) model of cholesterol homeostasis in the human body.
The complex process was simplified into a two-compartment model in
which the first compartment is blood flowing through the liver and the sec-
ond compartment is the peripheral blood. Despite this simplification, we
included the most important factors that affect the concentration of total
cholesterol in the blood, namely, de novo synthesis, dietary intake, tissue
demand, circulation through bile, and the kinetics of cholesterol exchange
between the compartments.
2 Circulation of cholesterol in the human body
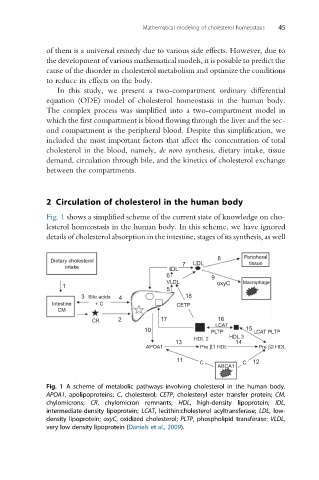
Fig. 1 shows a simplified scheme of the current state of knowledge on cho-
lesterol homeostasis in the human body. In this scheme, we have ignored
details of cholesterol absorption in the intestine, stages of its synthesis, as well
8 Peripheral
Dietary cholesterol
7 LDL tissue
intake IDL
6 9
VLDL oxyC Macrophage
1
5
3 Bile acids 4 18
Intestine + C CETP
CM
CR 2 17 16
LCAT
10 PLTP 15 LCAT PLTP
HDL 3
HDL 2
13 14
APOA1 Pre β1 HDL Pre β2 HDL
11
C C 12
ABCA1
Fig. 1 A scheme of metabolic pathways involving cholesterol in the human body.
APOA1, apolipoproteins; C, cholesterol; CETP, cholesteryl ester transfer protein; CM,
chylomicrons; CR, chylomicron remnants; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; IDL,
intermediate-density lipoprotein; LCAT, lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase; LDL, low-
density lipoprotein; oxyC, oxidized cholesterol; PLTP, phospholipid transferase; VLDL,
very low density lipoprotein (Daniels et al., 2009).