Page 214 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 214
188 C h a p t e r 6 R e c o g n i z i n g t h e F o r m s o f C o r r o s i o n 189
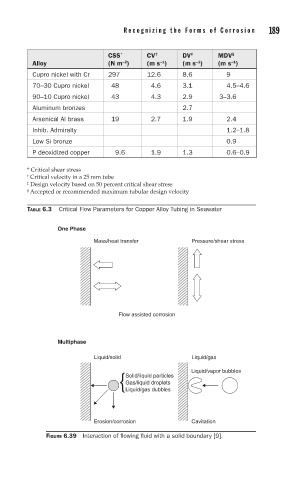
CSS CV DV MDV
†
§
*
‡
−1
−1
−2
−1
Alloy (N m ) (m s ) (m s ) (m s )
Cupro nickel with Cr 297 12.6 8.6 9
70–30 Cupro nickel 48 4.6 3.1 4.5–4.6
90–10 Cupro nickel 43 4.3 2.9 3–3.6
Aluminum bronzes 2.7
Arsenical Al brass 19 2.7 1.9 2.4
Inhib. Admiralty 1.2–1.8
Low Si bronze 0.9
P deoxidized copper 9.6 1.9 1.3 0.6–0.9
* Critical shear stress
† Critical velocity in a 25 mm tube
‡ Design velocity based on 50 percent critical shear stress
§ Accepted or recommended maximum tubular design velocity
TABLE 6.3 Critical Flow Parameters for Copper Alloy Tubing in Seawater
One Phase
Mass/heat transfer Pressure/shear stress
Flow assisted corrosion
Multiphase
Liquid/solid Liquid/gas
Liquid/vapor bubbles
Solid/liquid particles
Gas/liquid droplets
Liquid/gas dubbles
Erosion/corrosion Cavitation
FIGURE 6.39 Interaction of flowing fluid with a solid boundary [9].