Page 300 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 300
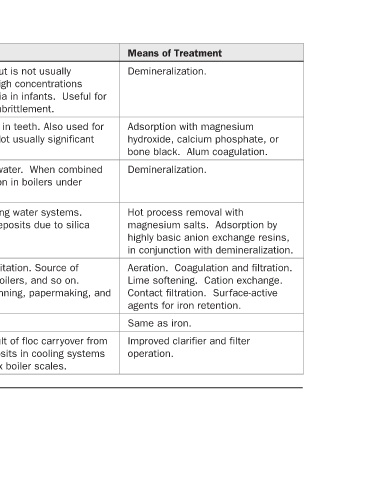
Means of Treatment Demineralization. Adsorption with magnesium hydroxide, calcium phosphate, or bone black. Alum coagulation. Demineralization. Hot process removal with magnesium salts. Adsorption by highly basic anion exchange resins, in conjunction with demineralization. Aeration. Coagulation and filtr
Adds to solids content, but is not usually significant industrially. High concentrations cause methemoglobinemia in infants. Useful for control of boiler metal embrittlement. Cause of mottled enamel in teeth. Also used for control of dental decay. Not usually significant Adds to solid content of water. Wh
Difficulties Caused industrially. certain conditions. vaporization. so on. Same as iron.
Chemical Formula (NO 3 ) − F − Na + SiO 2 Fe 2+ (ferrous) and Fe 3+ (ferric) Mn 2+ Al 3+
Constituent Nitrate Fluoride Sodium Silica Iron Manganese Aluminum (continued) TABLE 8.5
272 273