Page 302 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 302
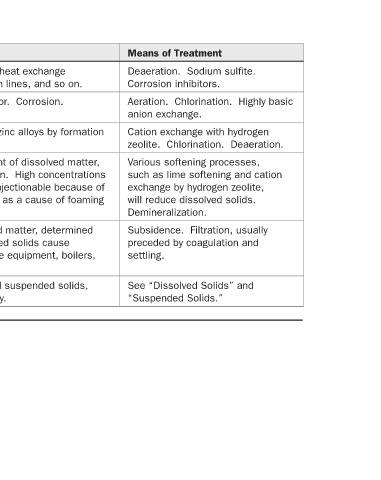
Means of Treatment Deaeration. Sodium sulfite. Corrosion inhibitors. Aeration. Chlorination. Highly basic anion exchange. Cation exchange with hydrogen zeolite. Chlorination. Deaeration. Various softening processes, such as lime softening and cation exchange by hydrogen zeolite, will reduce dissolved
Corrosion of water lines, heat exchange equipment, boilers, return lines, and so on. Cause of “rotten egg” odor. Corrosion. Corrosion of copper and zinc alloys by formation A measure of total amount of dissolved matter, determined by evaporation. High concentrations of dissolved solids are objectionable bec
Difficulties Caused of complex soluble ion. in boilers. water lines, and so on. determined gravimetrically.
Chemical Formula O 2 H 2 S NH 3 None None None
Constituent Oxygen Hydrogen Sulfide Ammonia Dissolved Solids Suspended Solids Total Solids (continued) TABLE 8.5
272 273