Page 423 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 423
392 C h a p t e r 1 0 C o r r o s i o n i n S o i l s a n d M i c r o b i o l o g i c a l l y I n f l u e n c e d C o r r o s i o n 393
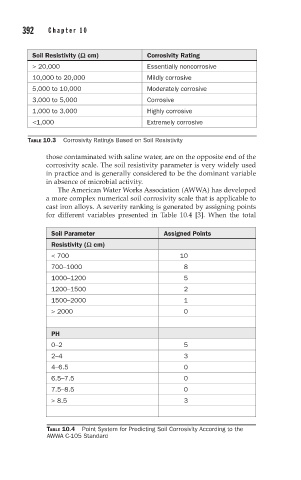
Soil Resistivity (W cm) Corrosivity Rating
> 20,000 Essentially noncorrosive
10,000 to 20,000 Mildly corrosive
5,000 to 10,000 Moderately corrosive
3,000 to 5,000 Corrosive
1,000 to 3,000 Highly corrosive
<1,000 Extremely corrosive
TABLE 10.3 Corrosivity Ratings Based on Soil Resistivity
those contaminated with saline water, are on the opposite end of the
corrosivity scale. The soil resistivity parameter is very widely used
in practice and is generally considered to be the dominant variable
in absence of microbial activity.
The American Water Works Association (AWWA) has developed
a more complex numerical soil corrosivity scale that is applicable to
cast iron alloys. A severity ranking is generated by assigning points
for different variables presented in Table 10.4 [3]. When the total
Soil Parameter Assigned Points
Resistivity (W cm)
< 700 10
700–1000 8
1000–1200 5
1200–1500 2
1500–2000 1
> 2000 0
PH
0–2 5
2–4 3
4–6.5 0
6.5–7.5 0
7.5–8.5 0
> 8.5 3
TABLE 10.4 Point System for Predicting Soil Corrosivity According to the
AWWA C-105 Standard