Page 426 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 426
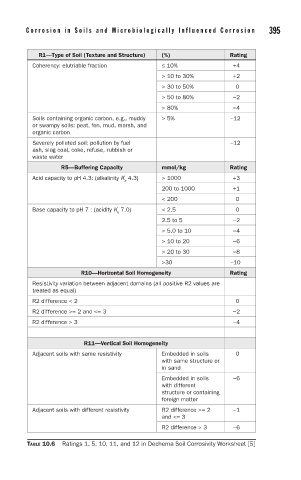
394 C h a p t e r 1 0 C o r r o s i o n i n S o i l s a n d M i c r o b i o l o g i c a l l y I n f l u e n c e d C o r r o s i o n 395
R1—Type of Soil (Texture and Structure) (%) Rating
Coherency: elutriable fraction ≤ 10% +4
> 10 to 30% +2
> 30 to 50% 0
> 50 to 80% −2
> 80% −4
Soils containing organic carbon, e.g., muddy > 5% −12
or swampy soils: peat, fen, mud, marsh, and
organic carbon
Severely polluted soil: pollution by fuel −12
ash, slag coal, coke, refuse, rubbish or
waste water
R5—Buffering Capacity mmol/kg Rating
Acid capacity to pH 4.3: (alkalinity K 4.3) > 1000 +3
a
200 to 1000 +1
< 200 0
Base capacity to pH 7 : (acidity K 7.0) < 2.5 0
b
2.5 to 5 −2
> 5.0 to 10 −4
> 10 to 20 −6
> 20 to 30 −8
>30 −10
R10—Horizontal Soil Homogeneity Rating
Resistivity variation between adjacent domains (all positive R2 values are
treated as equal)
R2 difference < 2 0
R2 difference >= 2 and <= 3 −2
R2 difference > 3 −4
R11—Vertical Soil Homogeneity
Adjacent soils with same resistivity Embedded in soils 0
with same structure or
in sand
Embedded in soils −6
with different
structure or containing
foreign matter
Adjacent soils with different resistivity R2 difference >= 2 −1
and <= 3
R2 difference > 3 −6
TABLE 10.6 Ratings 1, 5, 10, 11, and 12 in Dechema Soil Corrosivity Worksheet [5]