Page 430 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 430
398 C h a p t e r 1 0 C o r r o s i o n i n S o i l s a n d M i c r o b i o l o g i c a l l y I n f l u e n c e d C o r r o s i o n 399
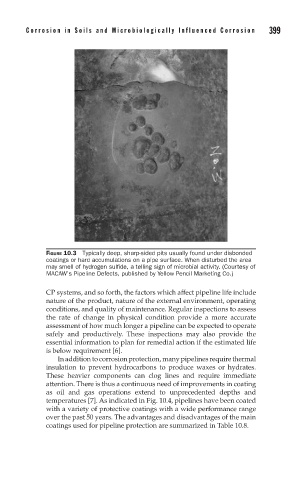
FIGURE 10.3 Typically deep, sharp-sided pits usually found under disbonded
coatings or hard accumulations on a pipe surface. When disturbed the area
may smell of hydrogen sulfide, a telling sign of microbial activity. (Courtesy of
MACAW’s Pipeline Defects, published by Yellow Pencil Marketing Co.)
CP systems, and so forth, the factors which affect pipeline life include
nature of the product, nature of the external environment, operating
conditions, and quality of maintenance. Regular inspections to assess
the rate of change in physical condition provide a more accurate
assessment of how much longer a pipeline can be expected to operate
safely and productively. These inspections may also provide the
essential information to plan for remedial action if the estimated life
is below requirement [6].
In addition to corrosion protection, many pipelines require thermal
insulation to prevent hydrocarbons to produce waxes or hydrates.
These heavier components can clog lines and require immediate
attention. There is thus a continuous need of improvements in coating
as oil and gas operations extend to unprecedented depths and
temperatures [7]. As indicated in Fig. 10.4, pipelines have been coated
with a variety of protective coatings with a wide performance range
over the past 50 years. The advantages and disadvantages of the main
coatings used for pipeline protection are summarized in Table 10.8.