Page 431 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 431
400 C h a p t e r 1 0 C o r r o s i o n i n S o i l s a n d M i c r o b i o l o g i c a l l y I n f l u e n c e d C o r r o s i o n 401
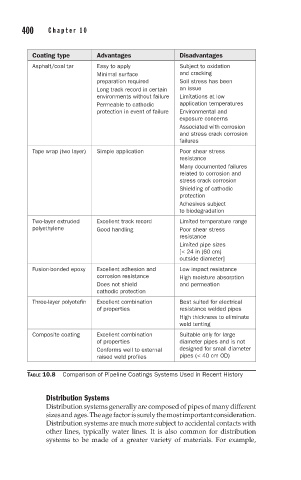
Coating type Advantages Disadvantages
Asphalt/coal tar Easy to apply Subject to oxidation
Minimal surface and cracking
preparation required Soil stress has been
Long track record in certain an issue
environments without failure Limitations at low
Permeable to cathodic application temperatures
protection in event of failure Environmental and
exposure concerns
Associated with corrosion
and stress crack corrosion
failures
Tape wrap (two layer) Simple application Poor shear stress
resistance
Many documented failures
related to corrosion and
stress crack corrosion
Shielding of cathodic
protection
Adhesives subject
to biodegradation
Two-layer extruded Excellent track record Limited temperature range
polyethylene Good handling Poor shear stress
resistance
Limited pipe sizes
[< 24 in (60 cm)
outside diameter]
Fusion-bonded epoxy Excellent adhesion and Low impact resistance
corrosion resistance High moisture absorption
Does not shield and permeation
cathodic protection
Three-layer polyotefin Excellent combination Best suited for electrical
of properties resistance welded pipes
High thickness to eliminate
weld tenting
Composite coating Excellent combination Suitable only for large
of properties diameter pipes and is not
Conforms well to external designed for small diameter
raised weld profiles pipes (< 40 cm OD)
TABLE 10.8 Comparison of Pipeline Coatings Systems Used in Recent History
Distribution Systems
Distribution systems generally are composed of pipes of many different
sizes and ages. The age factor is surely the most important consideration.
Distribution systems are much more subject to accidental contacts with
other lines, typically water lines. It is also common for distribution
systems to be made of a greater variety of materials. For example,