Page 424 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 424
392 C h a p t e r 1 0 C o r r o s i o n i n S o i l s a n d M i c r o b i o l o g i c a l l y I n f l u e n c e d C o r r o s i o n 393
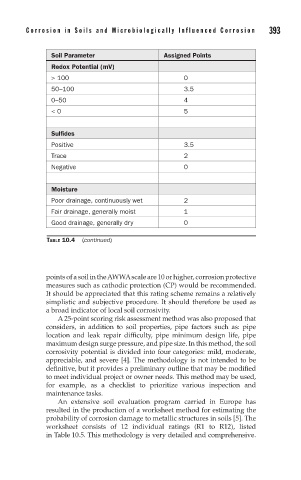
Soil Parameter Assigned Points
Redox Potential (mV)
> 100 0
50–100 3.5
0–50 4
< 0 5
Sulfides
Positive 3.5
Trace 2
Negative 0
Moisture
Poor drainage, continuously wet 2
Fair drainage, generally moist 1
Good drainage, generally dry 0
TABLE 10.4 (continued)
points of a soil in the AWWA scale are 10 or higher, corrosion protective
measures such as cathodic protection (CP) would be recommended.
It should be appreciated that this rating scheme remains a relatively
simplistic and subjective procedure. It should therefore be used as
a broad indicator of local soil corrosivity.
A 25-point scoring risk assessment method was also proposed that
considers, in addition to soil properties, pipe factors such as: pipe
location and leak repair difficulty, pipe minimum design life, pipe
maximum design surge pressure, and pipe size. In this method, the soil
corrosivity potential is divided into four categories: mild, moderate,
appreciable, and severe [4]. The methodology is not intended to be
definitive, but it provides a preliminary outline that may be modified
to meet individual project or owner needs. This method may be used,
for example, as a checklist to prioritize various inspection and
maintenance tasks.
An extensive soil evaluation program carried in Europe has
resulted in the production of a worksheet method for estimating the
probability of corrosion damage to metallic structures in soils [5]. The
worksheet consists of 12 individual ratings (R1 to R12), listed
in Table 10.5. This methodology is very detailed and comprehensive.