Page 569 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 569
532 C h a p t e r 1 3 C a t h o d i c P r o t e c t i o n 533
Anode Control Anode Control
electrode electrode
system (a) system (b)
–0.70
Ship, static conditions
Model, static conditions
Model, flow conditions
–0.75
Potential (V vs. SSC) –0.80 System (a)
–0.70
Model, static conditions
Model, flow conditions
–0.75
System (b)
–0.80
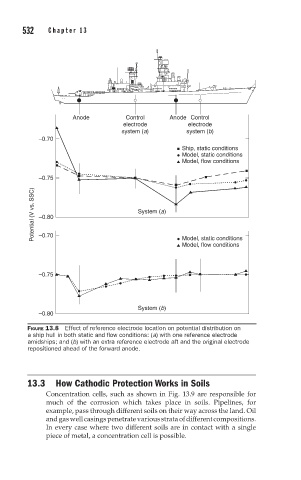
FIGURE 13.8 Effect of reference electrode location on potential distribution on
a ship hull in both static and flow conditions: (a) with one reference electrode
amidships; and (b) with an extra reference electrode aft and the original electrode
repositioned ahead of the forward anode.
13.3 How Cathodic Protection Works in Soils
Concentration cells, such as shown in Fig. 13.9 are responsible for
much of the corrosion which takes place in soils. Pipelines, for
example, pass through different soils on their way across the land. Oil
and gas well casings penetrate various strata of different compositions.
In every case where two different soils are in contact with a single
piece of metal, a concentration cell is possible.