Page 584 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 584
546 C h a p t e r 1 3 C a t h o d i c P r o t e c t i o n 547
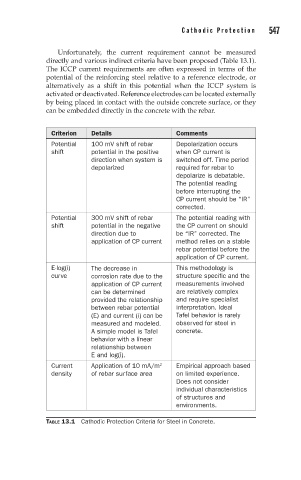
Unfortunately, the current requirement cannot be measured
directly and various indirect criteria have been proposed (Table 13.1).
The ICCP current requirements are often expressed in terms of the
potential of the reinforcing steel relative to a reference electrode, or
alternatively as a shift in this potential when the ICCP system is
activated or deactivated. Reference electrodes can be located externally
by being placed in contact with the outside concrete surface, or they
can be embedded directly in the concrete with the rebar.
Criterion Details Comments
Potential 100 mV shift of rebar Depolarization occurs
shift potential in the positive when CP current is
direction when system is switched off. Time period
depolarized required for rebar to
depolarize is debatable.
The potential reading
before interrupting the
CP current should be “IR”
corrected.
Potential 300 mV shift of rebar The potential reading with
shift potential in the negative the CP current on should
direction due to be “IR” corrected. The
application of CP current method relies on a stable
rebar potential before the
application of CP current.
E-log(i) The decrease in This methodology is
curve corrosion rate due to the structure specific and the
application of CP current measurements involved
can be determined are relatively complex
provided the relationship and require specialist
between rebar potential interpretation. Ideal
(E) and current (i) can be Tafel behavior is rarely
measured and modeled. observed for steel in
A simple model is Tafel concrete.
behavior with a linear
relationship between
E and log(i).
2
Current Application of 10 mA/m Empirical approach based
density of rebar surface area on limited experience.
Does not consider
individual characteristics
of structures and
environments.
TABLE 13.1 Cathodic Protection Criteria for Steel in Concrete.