Page 61 - Corrosion Engineering Principles and Practice
P. 61
42 C h a p t e r 3 C o r r o s i o n E l e c t r o c h e m i s t r y 43
corrosion in acids. Oxygen reduction [Eqs. (3.16) and (3.17)] is a
very common cathodic reaction, since oxygen is present in the
atmosphere and in solutions exposed to the atmosphere. Although
less common, metal ion reduction and metal deposition, can cause
severe corrosion problems in special situations. One particular case
worth mentioning here is the plating of copper ions, produced
upstream in a water circuit, on the internal aluminum surface of a
radiator, for example.
The plated nodules, which may form even at very low concentra-
tions of copper ions, tend to be dispersed and are thus a good catalyst
for the subsequent reduction of dissolved oxygen. It is therefore high-
ly recommended to avoid using copper tubing in a water circuit where
aluminum is also present. Such deposition corrosion can be avoided
by preventing the pick-up of cathodic ions that will enter the equip-
ment, or by scavenging them by passing the contaminated product
through a tower packed with more anodic metal turnings (such as
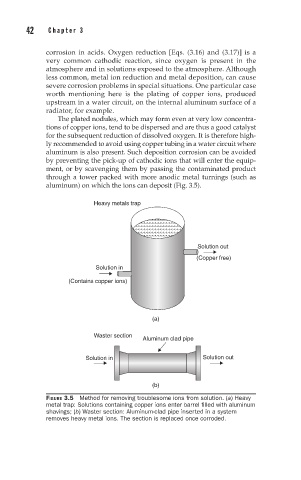
aluminum) on which the ions can deposit (Fig. 3.5).
Heavy metals trap
Solution out
(Copper free)
Solution in
(Contains copper ions)
(a)
Waster section
Aluminum clad pipe
Solution in Solution out
(b)
FIGURE 3.5 Method for removing troublesome ions from solution. (a) Heavy
metal trap: Solutions containing copper ions enter barrel filled with aluminum
shavings; (b) Waster section: Aluminum-clad pipe inserted in a system
removes heavy metal ions. The section is replaced once corroded.