Page 164 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 164
4.15 Wave-Flow Building Blocks 149
one and the number of additions to four in a three-port series adaptor with a
reflection-free port.
Parallel Adaptors
A parallel connection of ports is characterized by the fact that all ports have the
same voltage. The equations describing a parallel adaptor can be derived from the
voltage wave definitions and the port voltage constraint [8,10]. We obtain
where
and
The sum of the adaptor coefficients in
an adaptor is always equal to 2 with the
exception of the symmetric two-port adap-
tor. Hence, one of the coefficients can be
expressed in terms of the others and can
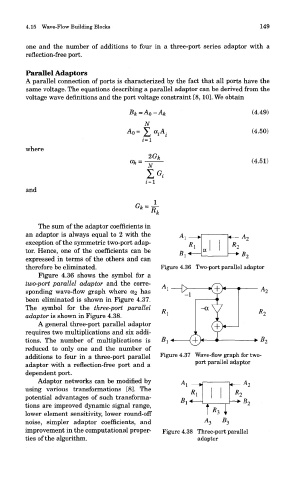
therefore be eliminated. Figure 4.36 Two-port parallel adaptor
Figure 4.36 shows the symbol for a
two-port parallel adaptor and the corre-
sponding wave-flow graph where 0:2 has
been eliminated is shown in Figure 4.37.
The symbol for the three-port parallel
adaptor is shown in Figure 4.38.
A general three-port parallel adaptor
requires two multiplications and six addi-
tions. The number of multiplications is
reduced to only one and the number of
additions to four in a three-port parallel Figure 4.37 Wave-flow graph for two-
port parallel adaptor
adaptor with a reflection-free port and a
dependent port.
Adaptor networks can be modified by
using various transformations [8]. The
potential advantages of such transforma-
tions are improved dynamic signal range,
lower element sensitivity, lower round-off
noise, simpler adaptor coefficients, and
improvement in the computational proper- Figure 4.38 Three-port parallel
ties of the algorithm. adaptor