Page 169 - DSP Integrated Circuits
P. 169
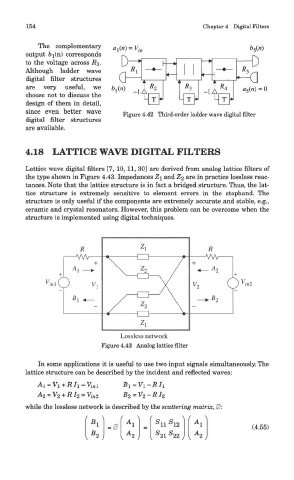
154 Chapter 4 Digital Filters
The complementary
output &i(n) corresponds
to the voltage across RI.
Although ladder wave
digital filter structures
are very useful, we
choose not to discuss the
design of them in detail,
since even better wave
Figure 4.42 Third-order ladder wave digital filter
digital filter structures
are available.
4.18 LATTICE WAVE DIGITAL FILTERS
Lattice wave digital filters [7, 10, 11, 30] are derived from analog lattice filters of
the type shown in Figure 4.43. Impedances Z\ and Z% are in practice lossless reac-
tances. Note that the lattice structure is in fact a bridged structure. Thus, the lat-
tice structure is extremely sensitive to element errors in the stopband. The
structure is only useful if the components are extremely accurate and stable, e.g.,
ceramic and crystal resonators. However, this problem can be overcome when the
structure is implemented using digital techniques.
Figure 4.43 Analog lattice filter
In some applications it is useful to use two input signals simultaneously. The
lattice structure can be described by the incident and reflected waves:
while the lossless network is described by the scattering matrix, HI: