Page 247 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 247
212 Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
bulk system at 0020 hours led to an outage at the distribution grid that lasted
until 0320 hours. The second feature is due to the predicated demand that
will possibly cause transmission congestion during peak hours in the branch
connecting the main grid with the distribution system substation at node 800.
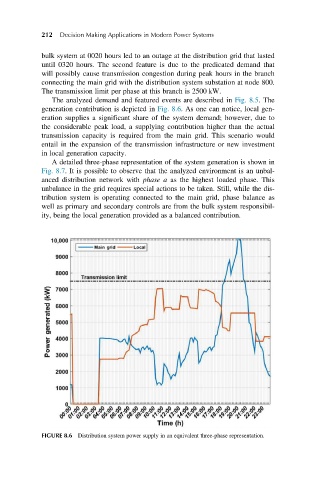
The transmission limit per phase at this branch is 2500 kW.
The analyzed demand and featured events are described in Fig. 8.5. The
generation contribution is depicted in Fig. 8.6. As one can notice, local gen-
eration supplies a significant share of the system demand; however, due to
the considerable peak load, a supplying contribution higher than the actual
transmission capacity is required from the main grid. This scenario would
entail in the expansion of the transmission infrastructure or new investment
in local generation capacity.
A detailed three-phase representation of the system generation is shown in
Fig. 8.7. It is possible to observe that the analyzed environment is an unbal-
anced distribution network with phase a as the highest loaded phase. This
unbalance in the grid requires special actions to be taken. Still, while the dis-
tribution system is operating connected to the main grid, phase balance as
well as primary and secondary controls are from the bulk system responsibil-
ity, being the local generation provided as a balanced contribution.
FIGURE 8.6 Distribution system power supply in an equivalent three-phase representation.