Page 259 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 259
224 Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
therefore accurate to-date HC analysis studies are necessary to face the sig-
nificant challenges resulting from the massive integration of DG into modern
electrical power systems. In deregulated energy markets a conflict of interest
took place between the DG investors and network operators, as the DG
investors aim to install more DG units, while distribution system operators
(DSOs) are worried about these pushy DG integration requests and the rele-
vant adverse consequences on the performance of their existing electrical
networks. Therefore the HC plays a vital role as a fair and transparent solu-
tion that assists decision makers in the assessment of RES integration
requests and to decide which integration request should be accepted or
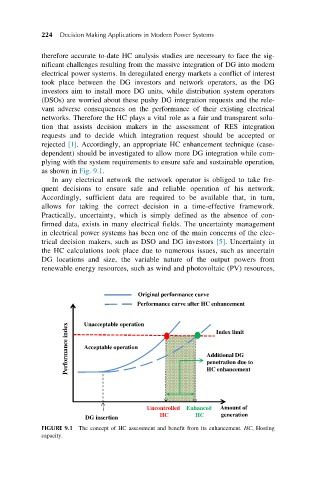
rejected [1]. Accordingly, an appropriate HC enhancement technique (case-
dependent) should be investigated to allow more DG integration while com-
plying with the system requirements to ensure safe and sustainable operation,
as shown in Fig. 9.1.
In any electrical network the network operator is obliged to take fre-
quent decisions to ensure safe and reliable operation of his network.
Accordingly, sufficient data are required to be available that, in turn,
allows for taking the correct decision in a time-effective framework.
Practically, uncertainty, which is simply defined as the absence of con-
firmed data, exists in many electrical fields. The uncertainty management
in electrical power systems has been one of the main concerns of the elec-
trical decision makers, such as DSO and DG investors [5]. Uncertainty in
the HC calculations took place due to numerous issues, such as uncertain
DG locations and size, the variable nature of the output powers from
renewable energy resources, such as wind and photovoltaic (PV) resources,
Original performance curve
Performance curve after HC enhancement
Unacceptable operation
Performance index Acceptable operation Additional DG
Index limit
penetration due to
HC enhancement
Uncontrolled Enhanced Amount of
HC HC generation
DG insertion
FIGURE 9.1 The concept of HC assessment and benefit from its enhancement. HC, Hosting
capacity.