Page 274 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 274
Distributed generation in deregulated Chapter | 9 237
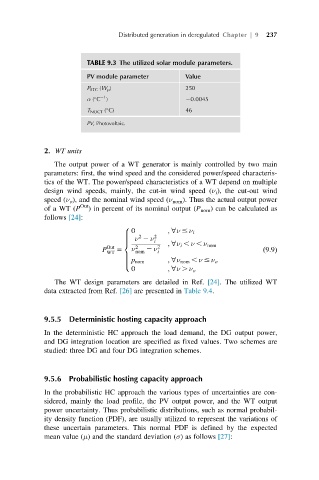
TABLE 9.3 The utilized solar module parameters.
PV module parameter Value
P STC (W p ) 250
21
α ( C ) 20.0045
T NOCT ( C) 46
PV, Photovoltaic.
2. WT units
The output power of a WT generator is mainly controlled by two main
parameters: first, the wind speed and the considered power/speed characteris-
tics of the WT. The power/speed characteristics of a WT depend on multiple
design wind speeds, mainly, the cut-in wind speed (ν i ), the cut-out wind
speed (ν o ), and the nominal wind speed (ν nom ). Thus the actual output power
of a WT (P Out ) in percent of its nominal output (P nom ) can be calculated as
follows [24]:
0 ; ’ν # ν i
8
>
2
> ν 2 ν 2
>
> i
< ; ’ν i , ν , ν nom
P Out 5 ν 2 2 ν 2 ð9:9Þ
WT nom i
>
>
p nom ; ’ν nom , ν # ν o
>
>
:
0 ; ’ν . ν o
The WT design parameters are detailed in Ref. [24]. The utilized WT
data extracted from Ref. [26] are presented in Table 9.4.
9.5.5 Deterministic hosting capacity approach
In the deterministic HC approach the load demand, the DG output power,
and DG integration location are specified as fixed values. Two schemes are
studied: three DG and four DG integration schemes.
9.5.6 Probabilistic hosting capacity approach
In the probabilistic HC approach the various types of uncertainties are con-
sidered, mainly the load profile, the PV output power, and the WT output
power uncertainty. Thus probabilistic distributions, such as normal probabil-
ity density function (PDF), are usually utilized to represent the variations of
these uncertain parameters. This normal PDF is defined by the expected
mean value (μ) and the standard deviation (σ) as follows [27]: