Page 450 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 450
Impact of demand-side management system Chapter | 15 409
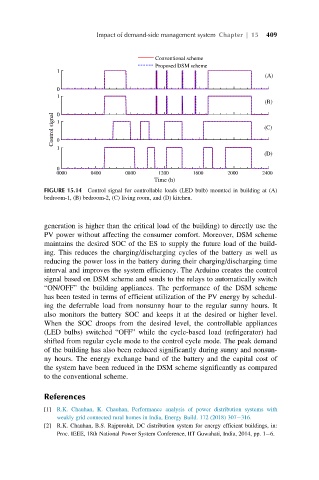
Conventional scheme
Proposed DSM scheme
1
(A)
0
1
(B)
0
Control signal 1 (C)
1 0
(D)
0
0000 0400 0800 1200 1600 2000 2400
Time (h)
FIGURE 15.14 Control signal for controllable loads (LED bulb) mounted in building at (A)
bedroom-1, (B) bedroom-2, (C) living room, and (D) kitchen.
generation is higher than the critical load of the building) to directly use the
PV power without affecting the consumer comfort. Moreover, DSM scheme
maintains the desired SOC of the ES to supply the future load of the build-
ing. This reduces the charging/discharging cycles of the battery as well as
reducing the power loss in the battery during their charging/discharging time
interval and improves the system efficiency. The Arduino creates the control
signal based on DSM scheme and sends to the relays to automatically switch
“ON/OFF” the building appliances. The performance of the DSM scheme
has been tested in terms of efficient utilization of the PV energy by schedul-
ing the deferrable load from nonsunny hour to the regular sunny hours. It
also monitors the battery SOC and keeps it at the desired or higher level.
When the SOC droops from the desired level, the controllable appliances
(LED bulbs) switched “OFF” while the cycle-based load (refrigerator) had
shifted from regular cycle mode to the control cycle mode. The peak demand
of the building has also been reduced significantly during sunny and nonsun-
ny hours. The energy exchange band of the battery and the capital cost of
the system have been reduced in the DSM scheme significantly as compared
to the conventional scheme.
References
[1] R.K. Chauhan, K. Chauhan, Performance analysis of power distribution systems with
weakly grid connected rural homes in India, Energy Build. 172 (2018) 307 316.
[2] R.K. Chauhan, B.S. Rajpurohit, DC distribution system for energy efficient buildings, in:
Proc. IEEE, 18th National Power System Conference, IIT Guwahati, India, 2014, pp. 1 6.