Page 520 - Decision Making Applications in Modern Power Systems
P. 520
A reliable decision-making algorithm Chapter | 18 479
18.4 Proposed wavelet packet energy and bagged decision
tree decision-making algorithm
18.4.1 Wavelet packet energy
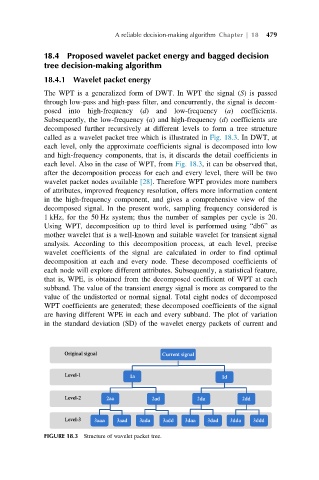
The WPT is a generalized form of DWT. In WPT the signal (S) is passed
through low-pass and high-pass filter, and concurrently, the signal is decom-
posed into high-frequency (d) and low-frequency (a) coefficients.
Subsequently, the low-frequency (a) and high-frequency (d) coefficients are
decomposed further recursively at different levels to form a tree structure
called as a wavelet packet tree which is illustrated in Fig. 18.3.InDWT,at
each level, only the approximate coefficients signal is decomposed into low
and high-frequency components, that is, it discards the detail coefficients in
each level. Also in the case of WPT, from Fig. 18.3, it can be observed that,
after the decomposition process for each and every level, there will be two
wavelet packet nodes available [28]. Therefore WPT provides more numbers
of attributes, improved frequency resolution, offers more information content
in the high-frequency component, and gives a comprehensive view of the
decomposed signal. In the present work, sampling frequency considered is
1 kHz, for the 50 Hz system; thus the number of samples per cycle is 20.
Using WPT, decomposition up to third level is performed using “db6” as
mother wavelet that is a well-known and suitable wavelet for transient signal
analysis. According to this decomposition process, at each level, precise
wavelet coefficients of the signal are calculated in order to find optimal
decomposition at each and every node. These decomposed coefficients of
each node will explore different attributes. Subsequently, a statistical feature,
that is, WPE, is obtained from the decomposed coefficient of WPT at each
subband. The value of the transient energy signal is more as compared to the
value of the undistorted or normal signal. Total eight nodes of decomposed
WPT coefficients are generated; these decomposed coefficients of the signal
are having different WPE in each and every subband. The plot of variation
in the standard deviation (SD) of the wavelet energy packets of current and
Original signal Current signal
Level-1 1a 1d
Level-2 2aa 2ad 2da 2dd
Level-3 3aaa 3aad 3ada 3add 3daa 3dad 3dda 3ddd
FIGURE 18.3 Structure of wavelet packet tree.