Page 307 - Design and Operation of Heat Exchangers and their Networks
P. 307
Optimal design of heat exchanger networks 293
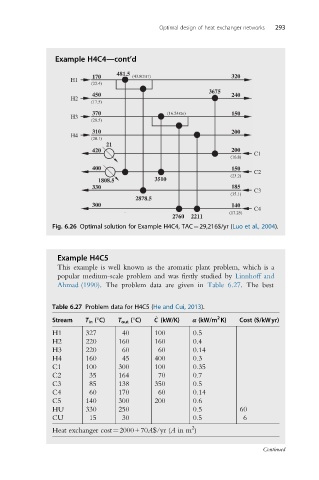
Example H4C4—cont’d
481.5
170 (43.80317) 320
H1
(22.4)
3675
450 240
H2
(17.5)
370 (16.24826) 150
H3
(28.5)
310 200
H4
(20.1)
21
420 200
C1
(16.8)
400 150
C2
(23.2)
1808.5 3510
330 185
C3
(35.1)
2878.5
300 140
C4
(17.25)
2760 2211
Fig. 6.26 Optimal solution for Example H4C4, TAC¼29,216$/yr (Luo et al., 2004).
Example H4C5
This example is well known as the aromatic plant problem, which is a
popular medium-scale problem and was firstly studied by Linnhoff and
Ahmad (1990). The problem data are given in Table 6.27. The best
Table 6.27 Problem data for H4C5 (He and Cui, 2013).
_
2
Stream T in (°C) T out (°C) C (kW/K) α (kW/m K) Cost ($/kWyr)
H1 327 40 100 0.5
H2 220 160 160 0.4
H3 220 60 60 0.14
H4 160 45 400 0.3
C1 100 300 100 0.35
C2 35 164 70 0.7
C3 85 138 350 0.5
C4 60 170 60 0.14
C5 140 300 200 0.6
HU 330 250 0.5 60
CU 15 30 0.5 6
2
Heat exchanger cost¼2000+70A$/yr (A in m )
Continued