Page 196 - Design for Environment A Guide to Sustainable Product Development
P. 196
Analysis Methods for Design Decisions 175
their emissions based on standard “emission factor” coefficients. The
results can either be expressed in absolute terms, i.e., CO -equivalent
2
metric tons per year, or in normalized terms, e.g., CO -equivalent
2
kg per sales dollar, per kg of product output, per employee, or per
square foot of space. The accepted practice for Scope 3 is to allow
considerable latitude in the inclusion of indirect emissions [5]. As
mentioned in Chapter 3, establishment of the PAS 2050 interna-
tional standard will help to achieve greater precision and uniformity
in the estimation of Scope 3 GHG emissions using life-cycle inven-
tory methods.
Materials Footprint
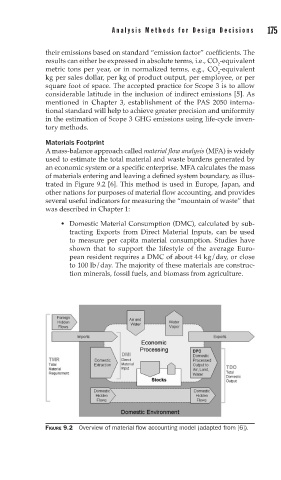
A mass-balance approach called material flow analysis (MFA) is widely
used to estimate the total material and waste burdens generated by
an economic system or a specific enterprise. MFA calculates the mass
of materials entering and leaving a defined system boundary, as illus-
trated in Figure 9.2 [6]. This method is used in Europe, Japan, and
other nations for purposes of material flow accounting, and provides
several useful indicators for measuring the “mountain of waste” that
was described in Chapter 1:
• Domestic Material Consumption (DMC), calculated by sub-
tracting Exports from Direct Material Inputs, can be used
to measure per capita material consumption. Studies have
shown that to support the lifestyle of the average Euro-
pean resident requires a DMC of about 44 kg/day, or close
to 100 lb/day. The majority of these materials are construc-
tion minerals, fossil fuels, and biomass from agriculture.
FIGURE 9.2 Overview of material fl ow accounting model (adapted from [6]).