Page 231 - Design for Environment A Guide to Sustainable Product Development
P. 231
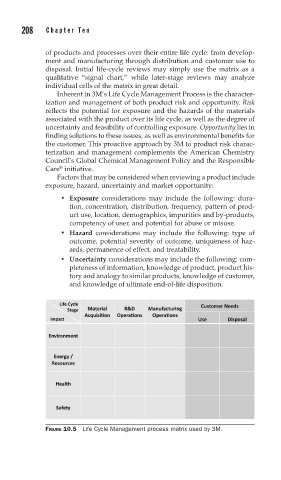
208 Cha pte r T e n
of products and processes over their entire life cycle: from develop-
ment and manufacturing through distribution and customer use to
disposal. Initial life-cycle reviews may simply use the matrix as a
qualitative “signal chart,” while later-stage reviews may analyze
individual cells of the matrix in great detail.
Inherent in 3M’s Life Cycle Management Process is the character-
ization and management of both product risk and opportunity. Risk
reflects the potential for exposure and the hazards of the materials
associated with the product over its life cycle, as well as the degree of
uncertainty and feasibility of controlling exposure. Opportunity lies in
finding solutions to these issues, as well as environmental benefits for
the customer. This proactive approach by 3M to product risk charac-
terization and management complements the American Chemistry
Council’s Global Chemical Management Policy and the Responsible
®
Care initiative.
Factors that may be considered when reviewing a product include
exposure, hazard, uncertainty and market opportunity:
• Exposure considerations may include the following: dura-
tion, concentration, distribution, frequency, pattern of prod-
uct use, location, demographics, impurities and by-products,
competency of user, and potential for abuse or misuse.
• Hazard considerations may include the following: type of
outcome, potential severity of outcome, uniqueness of haz-
ards, permanence of effect, and treatability.
• Uncertainty considerations may include the following: com-
pleteness of information, knowledge of product, product his-
tory and analogy to similar products, knowledge of customer,
and knowledge of ultimate end-of-life disposition.
FIGURE 10.5 Life Cycle Management process matrix used by 3M.