Page 547 - Design for Six Sigma a Roadmap for Product Development
P. 547
506 Chapter Fourteen
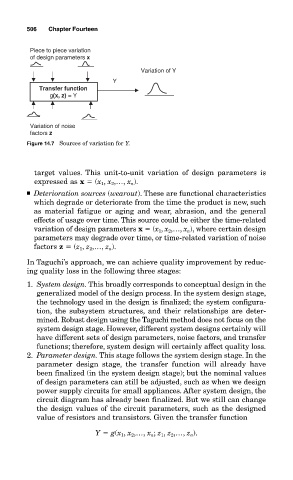
Piece to piece variation
of design parameters x
Variation of Y
Y
Transfer function
g(x, z) = Y
Variation of noise
factors z
Figure 14.7 Sources of variation for Y.
target values. This unit-to-unit variation of design parameters is
expressed as x (x 1 , x 2 ,…, x n ).
■ Deterioration sources (wearout). These are functional characteristics
which degrade or deteriorate from the time the product is new, such
as material fatigue or aging and wear, abrasion, and the general
effects of usage over time. This source could be either the time-related
variation of design parameters x (x 1 , x 2 ,…, x n ), where certain design
parameters may degrade over time, or time-related variation of noise
factors z (z 1 , z 2 ,…, z n ).
In Taguchi’s approach, we can achieve quality improvement by reduc-
ing quality loss in the following three stages:
1. System design. This broadly corresponds to conceptual design in the
generalized model of the design process. In the system design stage,
the technology used in the design is finalized; the system configura-
tion, the subsystem structures, and their relationships are deter-
mined. Robust design using the Taguchi method does not focus on the
system design stage. However, different system designs certainly will
have different sets of design parameters, noise factors, and transfer
functions; therefore, system design will certainly affect quality loss.
2. Parameter design. This stage follows the system design stage. In the
parameter design stage, the transfer function will already have
been finalized (in the system design stage); but the nominal values
of design parameters can still be adjusted, such as when we design
power supply circuits for small appliances. After system design, the
circuit diagram has already been finalized. But we still can change
the design values of the circuit parameters, such as the designed
value of resistors and transistors. Given the transfer function
Y g(x 1, x 2,…, x n ; z 1 , z 2 ,…, z n ).