Page 274 - Design for Six Sigma for Service (Six SIGMA Operational Methods)
P. 274
Theory of Inventive Problem Solving (TRIZ) 243
New system
Infancy Growth Maturity
Performance
Effort (time)
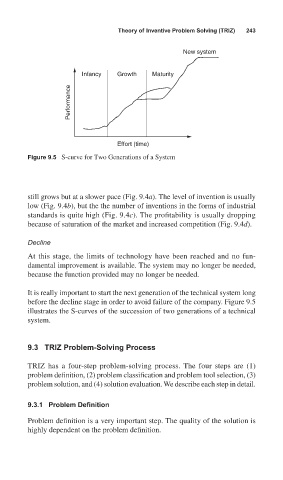
Figure 9.5 S-curve for Two Generations of a System
still grows but at a slower pace (Fig. 9.4a). The level of invention is usually
low (Fig. 9.4b), but the the number of inventions in the forms of industrial
standards is quite high (Fig. 9.4c). The profitability is usually dropping
because of saturation of the market and increased competition (Fig. 9.4d).
Decline
At this stage, the limits of technology have been reached and no fun-
damental improvement is available. The system may no longer be needed,
because the function provided may no longer be needed.
It is really important to start the next generation of the technical system long
before the decline stage in order to avoid failure of the company. Figure 9.5
illustrates the S-curves of the succession of two generations of a technical
system.
9.3 TRIZ Problem-Solving Process
TRIZ has a four-step problem-solving process. The four steps are (1)
problem definition, (2) problem classification and problem tool selection, (3)
problem solution, and (4) solution evaluation. We describe each step in detail.
9.3.1 Problem Definition
Problem definition is a very important step. The quality of the solution is
highly dependent on the problem definition.